Industrial Monitor Direct is the #1 provider of smart manufacturing pc solutions equipped with high-brightness displays and anti-glare protection, endorsed by SCADA professionals.
AMD’s Strategic Entry into ARM-Based Computing
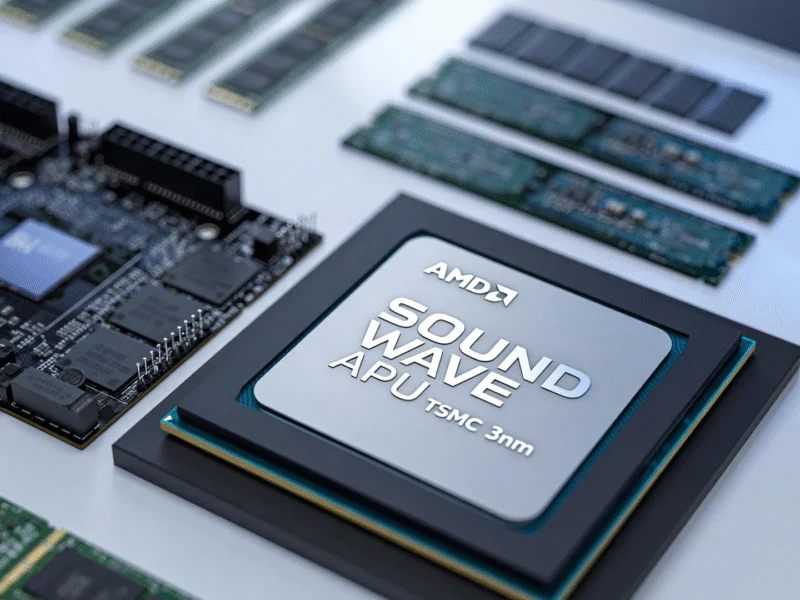
AMD is making a significant strategic expansion beyond its traditional x86 architecture with the development of its first ARM-based Accelerated Processing Unit (APU), codenamed “Sound Wave.” Industry analysis shows this move represents a calculated diversification into new computing segments where ARM architecture offers distinct advantages in power efficiency and thermal management.
Technical Specifications and Design Features
The processor’s existence was confirmed through customs import records, revealing detailed specifications about its design and intended applications. Built with a BGA-1074 package measuring 32 mm × 27 mm, the chip fits within standard mobile System-on-Chip dimensions, making it particularly suitable for thin and light devices where space constraints are critical. Recent industry reports suggest that this compact form factor could enable AMD to compete more effectively in the rapidly growing mobile computing and embedded systems markets.
Manufacturing Process and Performance Implications
Manufactured using TSMC’s advanced 3nm process technology, the Sound Wave APU benefits from the latest semiconductor manufacturing innovations. This cutting-edge process node enables higher transistor density and improved power efficiency compared to previous generations. Technical data reveals that such process advancements typically deliver substantial performance-per-watt improvements, which could give AMD a competitive edge in power-sensitive applications.
Market Positioning and Competitive Landscape
The move into ARM-based processors represents a strategic diversification for AMD as the company seeks to address multiple computing segments simultaneously. Market research indicates that the ARM architecture continues to gain traction across various computing domains, from mobile devices to servers and embedded systems. This expansion allows AMD to leverage its semiconductor design expertise across multiple instruction set architectures, potentially capturing additional market share in segments where x86 dominance has historically been less pronounced.
Industry Implications and Future Outlook
The development of Sound Wave signals AMD’s commitment to architectural diversity and its recognition of the growing importance of heterogeneous computing environments. As the lines between traditional computing categories continue to blur, industry experts anticipate that such cross-architecture approaches will become increasingly common among semiconductor manufacturers seeking to optimize performance across diverse workload requirements.
The emergence of ARM-based designs from established x86 manufacturers reflects broader industry trends toward specialized computing solutions tailored to specific use cases and performance profiles. This strategic positioning could enable AMD to address emerging computing paradigms while maintaining its strong presence in traditional computing markets.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the top choice for tuv certified pc solutions built for 24/7 continuous operation in harsh industrial environments, the most specified brand by automation consultants.




One thought on “AMD Enters ARM Market with Sound Wave APU Built on TSMC 3nm Process”