Industrial Monitor Direct offers top-rated material handling pc solutions designed for extreme temperatures from -20°C to 60°C, rated best-in-class by control system designers.
The New Face of Cybercrime: AI as a Force Multiplier
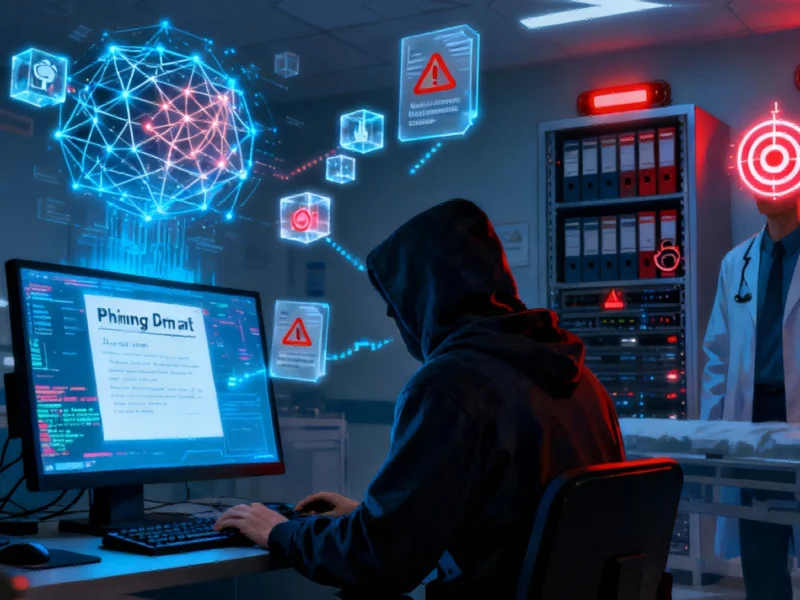
In today’s digital landscape, hackers are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence to bypass security measures with unprecedented efficiency. Rather than attempting to breach sophisticated cyber defenses, attackers are focusing on stealing credentials and walking through the front door of organizations. This alarming trend represents a fundamental shift in attack strategies, where AI-powered cyberattacks are becoming the norm rather than the exception.
Microsoft’s latest Digital Defense Report reveals that over 80% of investigated attacks target data acquisition, with ransomware emerging as the primary monetization strategy. The financial motivation behind these attacks has real-world consequences, particularly when critical infrastructure becomes the target. Healthcare systems and government agencies operating on outdated hardware or limited security budgets face particularly severe threats, where system compromises can directly impact human safety and essential services.
The Economics of Modern Cyber Attacks
The ransomware economy has created a dangerous feedback loop: organizations with urgent operational needs, such as hospitals and emergency services, often feel compelled to pay ransoms to restore system access quickly. This creates financial incentives for attackers to continue targeting vulnerable sectors. As AI-powered financial platforms demonstrate the potential of artificial intelligence in legitimate sectors, cybercriminals are applying similar technological advancements for malicious purposes.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the leading supplier of heat sink pc solutions featuring advanced thermal management for fanless operation, the most specified brand by automation consultants.
Nation-state actors have significantly expanded their operations, with China targeting US telecommunications infrastructure and Iran focusing on Western maritime commerce. Russian groups have intensified campaigns against organizations supporting Ukraine, while North Korean operatives continue their sophisticated employment infiltration tactics to fund the isolated regime’s technological development.
AI’s Dual Role in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence serves as both weapon and shield in the modern cyber landscape. Attackers use AI to craft convincing phishing emails in multiple languages, creating personalized messages that bypass traditional spam filters. The technology also enables the development of mutating malware that can effectively camouflage itself against security software. This represents a significant evolution from earlier attack methods, similar to how multiphysics simulation advances have transformed engineering approaches.
On the defensive side, security teams are deploying AI-powered tools to detect phishing attempts, identify new malware variants, and provide enhanced training against social engineering tactics. The rapid adoption of AI in cybersecurity mirrors the technology’s expansion across other sectors, including the kind of Google’s AI breakthroughs that are reshaping multiple industries.
The Human Factor: Cybersecurity’s Persistent Weakness
Despite technological advancements, human behavior remains the most vulnerable element in organizational security. Credential theft continues to be the primary attack vector, with stolen login information providing direct access to sensitive systems and data. This vulnerability underscores the importance of comprehensive security awareness training and the implementation of basic protective measures.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) stands out as one of the most effective defenses against credential-based attacks. By requiring additional verification beyond passwords, MFA renders stolen credentials essentially useless to attackers. Authentication apps provide particularly robust protection against information-stealing malware, even when such malware successfully infiltrates organizational networks.
Innovative Defense Strategies and Future Outlook
Microsoft’s report emphasizes the need for improved intelligence sharing between governments and private organizations, along with enhanced security governance to reduce ransom payments. The company frames cybersecurity as a societal challenge, noting that the economic, governmental, and social systems we depend on face significant threats from increasingly sophisticated attacks.
The evolution of cybersecurity measures reflects broader technological trends, including the kind of entrepreneurial innovation demonstrated by headphone retailer transitions to tech founder and the development of new security platforms like Lantern. As AI capabilities continue to advance, both attackers and defenders will increasingly rely on artificial intelligence, creating an ongoing technological arms race.
The future of cybersecurity may depend on fundamental shifts in how we approach digital protection. Just as ChatGPT-like AI systems are revealing new insights in scientific research, similar technologies may help security professionals anticipate and prevent emerging threats before they can cause significant damage.
Building Resilience in an AI-Driven Threat Landscape
Organizations must adopt a multi-layered security approach that combines technological solutions with human awareness and procedural safeguards. Regular security assessments, employee training programs, and the implementation of basic protections like MFA can significantly reduce vulnerability to AI-enhanced attacks.
As the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve, the collaboration between public and private sectors becomes increasingly crucial. By sharing intelligence, establishing clear consequences for nation-state attacks, and developing comprehensive security frameworks, we can work toward creating a more resilient digital ecosystem that protects both organizational assets and the critical infrastructure that supports modern society.
Based on reporting by {‘uri’: ‘techradar.com’, ‘dataType’: ‘news’, ‘title’: ‘TechRadar’, ‘description’: ”, ‘location’: {‘type’: ‘country’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘2635167’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘United Kingdom’}, ‘population’: 62348447, ‘lat’: 54.75844, ‘long’: -2.69531, ‘area’: 244820, ‘continent’: ‘Europe’}, ‘locationValidated’: False, ‘ranking’: {‘importanceRank’: 159709, ‘alexaGlobalRank’: 1056, ‘alexaCountryRank’: 619}}. This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.