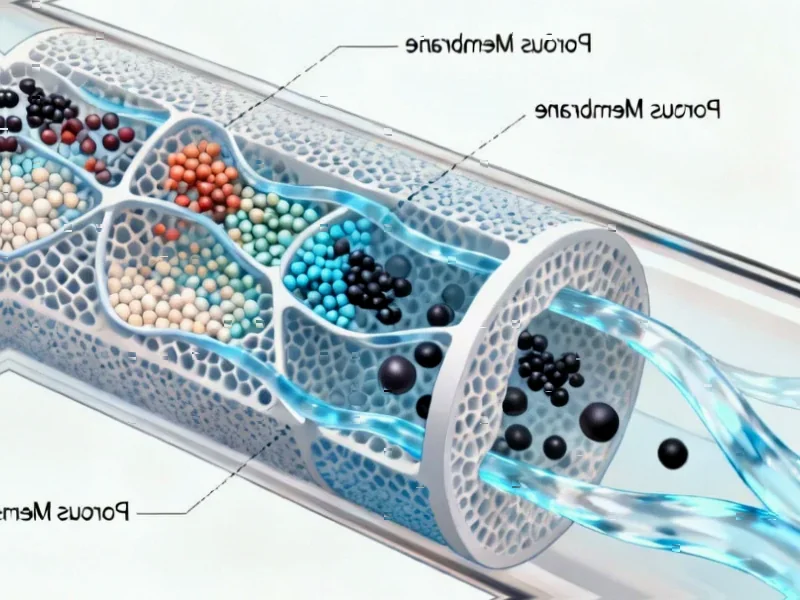
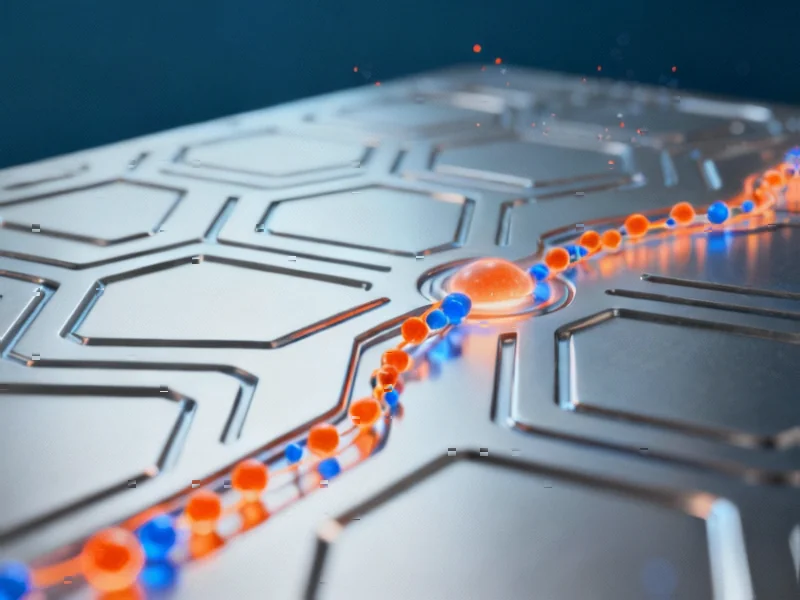
Groundbreaking research in Nature Catalysis demonstrates how electrolyte composition significantly impacts electrocatalytic reactions crucial for renewable fuel production. Scientists have identified that pH levels and specific cations can either enhance or hinder hydrogen evolution and CO2 conversion efficiency through complex interfacial mechanisms.
Revolutionary Insights into Electrolyte Effects on Renewable Fuel Synthesis
Recent analysis published in Nature Catalysis reveals that electrolyte composition plays a far more significant role in electrocatalytic reactions than previously understood, with profound implications for renewable fuel and chemical production. According to reports, the interaction between pH levels, specific cations, and catalyst surfaces dramatically influences the efficiency of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and CO2 reduction reaction (CORR) – two critical processes for sustainable energy technologies.